NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area| PDF Download
On this page, you will find Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions which will guide student in a better way and get a deeper understanding of various topics. You can figure out the latest marking scheme and prepare your answers as per the demand. You can download PDF of Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area NCERT Solutions that help you in analyzing the problems and answering it with precision and the right concepts.
Chapter 11 NCERT Solutions will be helpful in the preparation of examinations. It is a good way through which one can build their basic knowledge. These NCERT Solutions are updated according to the latest NCERT Class 8 Maths textbook and syllabus.

Exercise 11.1
1. The length and breadth of a rectangular piece of land are 500 m and 300 m respectively. Find:
(i) Its area.
(ii) The cost of the land, if 1 m2 of the land costs Rs 10,000.
Answer
From the question it is given that,
Length of the rectangular piece of land = 500 m
Breadth of the rectangular piece of land = 300 m
Then,
(i) Area of rectangle = Length × Breadth
= 500 × 300
= 15,0000 m2
(ii) Cost of the land for 1 m2 = Rs. 10000
Cost of the land for 150000 m2 = 10000 × 150000
= Rs. 15,00000000.
2. Find the area of a square park whose perimeter is 320 m.
Answer
From the question it is given that,
Perimeter of the square park = 320 m
4 × Length of the side of park = 320 m
Then,
Length of the side of park = 320/4 = 80 m
So, Area of the square park = (length of the side of park)2 = (80)2 m2 = 6400 m2
3. Find the breadth of a rectangular plot of land, if its area is 440 m2 and the length is 22 m. Also find its perimeter.
Answer
Area of rectangular park = 440 m2
⇒ length × breadth = 440 m2
⇒ 22 × breadth = 440
⇒ breadth = 440/20 = 20 m
Now, Perimeter of rectangular park
= 2 [length + breadth]
= 2 [22 + 20]
= 2 × 42 = 84 m
Thus, the perimeter of rectangular park is 84 m.
4. The perimeter of a rectangular sheet is 100 cm. If the length is 35 cm, find its breadth. Also find the area.
Answer
Perimeter of the rectangular sheet = 100 cm
⇒ 2 (length + breadth) = 100 cm
⇒ 2 (35 + breadth) = 100
⇒ 35 + breadth = 100/2
⇒ 35 + breadth = 50
⇒ breadth = 50 - 35
⇒ breadth = 15 cm
Now, Area of rectangular sheet = length x breadth
= 35 × 15 = 525 cm2
Thus, breadth and area of rectangular sheet are 15 cm and 525 cm2 respectively.
5. The area of a square park is the same as a rectangular park. If the side of the square park is 60 m and the length of the rectangular park is 90 cm, find the breadth of the rectangular park.
Answer
Given:
The side of the square park = 60 m
The length of the rectangular park = 90 m
According to the question,
Area of square park = Area of rectangular park
⇒ side × side = length × breadth
⇒ 60 × 60 = 90 × breadth
⇒ breadth = 60 × 60/ = 40m
Thus, the breadth of the rectangular park is 40 m.
6. A wire is in the shape of a rectangle. Its length is 40 cm and breadth is 22 cm. If the same wire is rebent in the shape of a square, what will be the measure of each side. Also find which shape encloses more area?
Answer
According to the question,
Perimeter of square = Perimeter of rectangle
⇒ 4 × side = 2 (length + breadth)
⇒ 4 × side = 2 (40 + 22)
⇒ 4 × side = 2 × 62
⇒ side = 2 × 62/4 = 31 cm
Thus, the side of the square is 31 cm.
Now, Area of rectangle = length × breadth = 40 × 22 = 880 cm2
And Area of square = side × side = 31 × 31 = 961 cm2
Therefore, on comparing, the area of square is greater than that of rectangle.
7. The perimeter of a rectangle is 130 cm. If the breadth of the rectangle is 30 cm, find its length. Also, find the area of the rectangle.
Answer
Perimeter of rectangle = 130 cm
⇒ 2 (length + breadth) = 130 cm
⇒ 2 (length + 30) = 130
⇒ length + 30 = 130/2
⇒ length + 30 = 65
⇒ length = 65 - 30 = 35 cm
Now area of rectangle = length × breadth = 35 × 30 = 1050 cm2
Thus, the area of rectangle is 1050 cm2.
8. A door of length 2 m and breadth 1 m is fitted in a wall. The length of the wall is 4.5 m and the breadth is 3.6 m. Find the cost of white washing the wall, if the rate of white washing the wall is Rs 20 per m2.

Answer
Area of rectangular door = length × breadth = 2 m × 1 m = 2 m2
Area of wall including door = length × breadth = 4.5 m × 3.6 m = 16.2 m2
Now, Area of wall excluding door = Area of wall including door - Area of door = 16.2-2 = 14.2 m2
Since, the rate of white washing of 1 m2 the wall = Rs 20
Therefore, the rate of white washing of 14.2 m2 the wall = 20 × 14.2 = Rs 284
Thus, the cost of white washing the wall excluding the door is Rs 284.
Exercise 11.2
1. Find the area of each of the following parallelograms:

Answer
We know that the area of parallelogram = base x height
(a) Here base = 7 cm and height = 4 cm
∴ Area of parallelogram = 7×4 = 28 cm2
(b) Here base = 5 cm and height = 3 cm
∴ Area of parallelogram = 5×3 = 15 cm2
(c) Here base = 2.5 cm and height = 3.5 cm
∴ Area of parallelogram = 2.5 × 3.5 = 8.75 cm2
(d) Here base = 5 cm and height = 4.8 cm
∴ Area of parallelogram = 5 × 4.8 = 24 cm2
(e) Here base = 2 cm and height = 4.4 cm
∴ Area of parallelogram = 2 × 4.4 = 8.8 cm2
2. Find the area of each of the following triangles:

Answer
We know that the area of triangle
= 1/2×base×height
(a) Here, base = 4 cm and height = 3 cm
∴ Area of triangle
= 1/2×4×3 = 6 cm2
(b) Here, base = 5 cm and height = 3.2 cm
∴ Area of triangle
= 1/2×5×3.2 = 8 cm2
(c) Here, base = 3 cm and height = 4 cm
∴ Area of triangle
= 1/2×3×4 = 6 cm2
(d) Here, base = 3 cm and height = 2 cm
∴ Area of triangle
= 1/2×3×2 = 3 cm2
3. Find the missing values:
| S. No. | Base | Height | Area of the parallelogram |
| a. | 20 cm | 246 cm2 | |
| b. | 15 cm | 154.5 cm2 | |
| c | 84 cm | 48.72 cm2 | |
| d. | 15.6 cm | 16.72 cm2 |
Answer
We know that the area of parallelogram = base x height
(a) Here, base = 20 cm and area = 246 cm2
∴ Area of parallelogram = base × height
⇒ 246 = 20 × height
⇒ height = 246/20 = 12.3 cm
(b) Here, height = 15 cm and area = 154.5 cm2
∴ Area of parallelogram = base × height
⇒ 154.5 = base × 15
⇒ base = 154.5/15 = 10.3 cm
(c) Here, height = 8.4 cm and area = 48.72 cm2
∴ Area of parallelogram = base × height
⇒ 48.72 = base × 8.4
⇒ base = 48.72/8.4 = 5.8 cm
(d) Here, base = 15.6 cm and area = 16.38 cm2
∴ Area of parallelogram = base × height
⇒ 16.38 = 15.6 × height
⇒ height = 16.38/15.6 = 1.05 cm
Thus, the missing values are:
| S. No. | Base | Height | Area of the parallelogram |
| a. | 20 cm | 12.3 cm | 246 cm2 |
| b. | 10.3 cm | 15 cm | 154.5 cm2 |
| c | 5.8 cm | 84 cm | 48.72 cm2 |
| d. | 15.6 cm | 1.05 | 16.72 cm2 |
4. Find the missing values:
| Base | Height | Area of triangle |
| 15 cm | ______ | 87 cm2 |
| _____ | 31.4 mm | 1256 mm2 |
| 22 cm | _____ | 170.5 cm2 |
Answer
We know that the area of triangle
= /2 × base × height
= /2 × base × height
In first row, base = 15 cm and area = 87 cm2
∴ 87 = 1/2 × 15 × height
⇒ height = 87 × 2/15 = 11.6 cm
In second row, height = 31.4 mm and area = 1256 mm2
∴ 1256 = 1/2 × base × 31.4
⇒ base = 1256 × 2/31.4 = 80 mm
In third row, base = 22 cm and area = 170.5 cm2
∴ 170.5 = 1/2 × 22 × height
⇒ height = 170.5 × 2/22 = 15.5 cm
Thus, the missing values are:
| Base | Height | Area of triangle |
| 15 cm | 11.6 cm | 87 cm2 |
| 80 mm | 31.4 mm | 1256 mm2 |
| 22 cm | 15.5 cm | 170.5 cm2 |
5. PQRS is a parallelogram (Fig 11.23), QM is the height from Q to SR and QN is the height from Q to PS. If SR = 12 cm and QM = 7.6 cm. Find:
(a) the area of the parallelogram PQRS
(b) QN, if PS = 8 cm

Answer
Given:
SR = 12 cm, QM = 7.6 cm, PS = 8 cm,
(a) Area of parallelogram = base × height
= 12 x 7.6 = 91.2 cm2
(b) Area of parallelogram = base × height
⇒ 91.2 = 8 × QN
⇒ QN = 91.2/8 = 11.4 cm
6. DL and BM are the heights on sides AB and AD respectively of parallelogram ABCD (Fig 11.24). If the area of the parallelogram is 1470 cm2, AB = 35 cm and AD = 49 cm, Find the length of BM and DL.
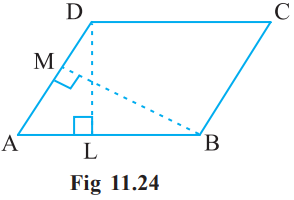
Answer
Given:
Area of parallelogram = 1470 cm2
Base (AB) = 35 cm and base (AD) = 49 cm
Since Area of parallelogram = base × height
⇒ 1470 = 35 × DL
⇒ DL = 1470/35
⇒ DL = 42 cm
Again, Area of parallelogram = base × height
⇒ 1470 = 49 × BM
⇒ BM = 1470/49
⇒ BM = 30 cm
Thus, the lengths of DL and BM are 42 cm and 30 cm respectively.
7. Δ ABC is right angled at A (Fig 11.25). AD is perpendicular to BC. If AB = 5 cm, BC = 13 cm and AC = 12 cm, find the area of Δ ABC. Also, find the length of AD.

Answer
Area = 1/2 × Base × Height = 1/2 × 5 × 12
= 30 cm2
Also, area of triangle = 1/2 × AD × BC
30 = 1/2 × AD × 13
30×2/13 = AD
AD = 4.6 cm
8. ΔABC is isosceles with AB = AC = 7.5 cm and BC = 9 cm (Fig 11.26). The height AD from A to BC, is 6 cm. Find the area of ΔABC. What will be the height from C to AB i.e., CE?

Answer
In ΔABC, AD = 6 cm and BC = 9 cm
Area of triangle = 1/2 × base × height = 1/2 × BC × AD
= 1/2 × 9 × 6 = 27 cm2
Again, Area of triangle 1/2 × base × height = 1/2 × AB × CE
⇒ 27 = 1/2 × 7.5 × CE
⇒ CE = 27×2/7.5
⇒ CE = 7.2 cm.
Thus, height from C to AB i.e., CE is 7.2 cm.
Exercise 11.3
1. Find the circumference of the circles with the following radius: (Take π = 22/7)
(a) 14 cm
(b) 28 mm
(c) 21 cm
Answer
(a) A circumference of the circle = 2πr = 2×22/7×14 = 88 cm
(b) A circumference of the circle = 2πr = 2×22/7×28 = 176 cm
(c) A circumference of the circle = 2πr = 2×22/7×21 = 132 cm
2. Find the area of the following circles, given that: (Take π = 22/7)
(a) radius = 14 mm
(b) diameter = 49 m
(c) radius = 5 cm
Answer
(a) Area of Circle = πr2 = 22/7 × 14 × 14
= 22 × 2 × 14
= 616 mm2
(b) Diameter = 49 m
∴ radius = 49/2 = 24.5 cm
∴ Area of Circle = πr2 = 22/7 × 24.5 × 24.5
= 22 × 3.5 × 24.5
= 1886.5 m2
(c) Area of Circle = πr2 = 22/7 × 5 × 5
= 550/7 cm2
3. If the circumference of a circular sheet is 154 m, find its radius. Also, find the area of the sheet. (Take π = 22/7)
Answer
Circumference of the circular sheet = 154 m
⇒ 2πr = 154 m
⇒ r = 154/2π
⇒ r = 154×7/2×22 = 24.5 m
Now, Area of circular sheet = πr2 = 22/7×24.5×24.5
= 22 x 3.5 x 24.5 = 1886.5 m2
Thus, the radius and area of circular sheet are 24.5 m and 1886.5 m2 respectively.
4. A gardener wants to fence a circular garden of diameter 21 m. Find the length of the rope he needs to purchase if he makes 2 rounds of a fence. Also, find the costs of the rope, if it cost Rs 4 per meter. (Take π = 22/7)
Answer
Diameter of the circular garden = 21 m
∴ Radius of the circular garden = 21/2 m
Now, Circumference of a circular garden = 2πr = 2×22/7×21/2
= 22 × 3 = 66 m
The gardener makes 2 rounds of a fence so the total length of the rope of fencing
= 2 × 2πr
= 2 × 66 = 132 m
Since, the cost of 1 meter rope = Rs 4
Therefore, Cost of 132 meter rope = 4 × 132 = Rs 528.
5. From a circular sheet of radius 4 cm, a circle of radius 3 cm is removed. Find the area of the remaining sheet. (Take π = 3.14)
Answer
Radius of circular sheet (R) = 4 cm and radius of removed circle (r) = 3 cm
Area of the remaining sheet = Area of a circular sheet - Area of removed circle
= πR2 - πr2 = π(R2 - r2)
= π(42 - 32) = π(16 - 9)
= 3.14 × 7 = 21.98 cm2
Thus, the area of the remaining sheet is 21.98 cm2.
6. Saima wants to put lace on the edge of a circular table cover of diameter 1.5 m. Find the length of the lace required and also find its cost if one meter of the lace costs Rs 15. (Take π = 3.14)
Answer
Diameter of the circular table cover = 1.5 m
∴ Radius of the circular table cover = 1.5/2 m
Circumference of circular table cover = 2πr = 2 × 3.14 × 1.5/2 = 4.71 m
Therefore, the length of required lace is 4.71 m.
Now the cost of 1 m lace = Rs 15
Then the cost of 4.71 m lace = 15 × 4.71 = Rs 70.65
Hence, the cost of 4.71 m lace is Rs 70.65.
7. Find the perimeter of the adjoining figure, which is a semicircle including its diameter.

Answer
Diameter = 10 cm
Radius = 10/2 = 5 cm
According to question,
Perimeter of figure = Circumference of semicircle + diameter
= πr + D
= 22/7 × 5 +10 = 110/7 = 10
= 110/70 /7 = 180/7 = 25.71 cm
Thus, the perimeter of the given figure is 25.71 cm.
8. Find the cost of polishing a circular table-top of diameter 1.6 m, if the rate of polishing is Rs 15/m2. (Take π = 3.14)
Answer
Diameter of the circular table top = 1.6 m
Radius of the circular table top = 1.6/2 = 0.8 m
Area of circular table top = πr2 = 3.14 × 0.8 x 0.8 = 2.0096 m2
Now, the cost of polishing 1 m2 = Rs 15
Then cost of polishing 2.0096 m2 = 15 × 2.0096 = Rs 30.14 (approx.)
Thus, The cost of polishing a circular table top is Rs 30.14 (approx.)
9. Shazli took a wire of length 44 cm and bent it into the shape of a circle. Find the radius of that circle. Also, find its area. If the same wire is bent into the shape of a square, what will be the length of each of its sides? Which figure encloses more area, the circle or the square? (Take π = 22/7)
Answer
Total length of the wire = 44 cm
∴ The circumference of the circle = 2πr = 44 cm
⇒ 2 × 22/7 × r = 44
⇒ r = 44×7/2×22 = 7 cm
Now Area of the circle = πr2
= 22/7 × 7 × 7 = 154 cm2
Now the wire is converted into the square.
The perimeter of square = 44 cm
⇒ 4 × side = 44
⇒ side = 44/4 = 11 cm
Now, area of square = side x side = 11 x 11 = 121 cm2
Therefore, on comparing, the area of the circle is greater than that of a square, so the circle encloses more area.
10. From a circular card sheet of radius 14 cm, two circles of radius 3.5 cm and a rectangle of length 3 cm and breadth 1 cm are removed (as shown in the adjoining figure). Find the area of the remaining sheet. (Take π = 22/7)

Answer
Radius of circular sheet (R) = 14 cm and Radius of smaller circle (r) = 3.5 cm
Length of rectangle (l) = 3 cm and breadth of rectangle (b) = 1 cm
According to question,
Area of remaining sheet = Area of circular sheet- (Area of two smaller circle + Area of rectangle)
= πr2 - [2(πr2)+(l+b)]
= 22/7 × 14 × 14 - [(2×22/7×3.5×3.5)-(3×1)]
=22×14×2 - [44×0.5×3.5+3]
=616 - 80
= 536 cm2
Therefore, the area of the remaining sheet is 536 cm2.
11. A circle of radius 2 cm is cut out from a square piece of an aluminum sheet of side 6 cm. What is the area of the leftover aluminum sheet? (Take π = 3.14)
Answer
Radius of circle = 2 cm and side of aluminium square sheet = 6 cm
According to question,
Area of aluminum sheet left = Total area of aluminum sheet - Area of circle
= side × side - πr2
= 6 × 6 - 22/7 × 2 × 2
= 36 -12.56
= 23.44 cm2
Therefore, the area of the aluminum sheet left is 23.44 cm2.
12. The circumference of a circle is 31.4 cm. Find the radius and the area of the circle. (Take π = 3.14)
Answer
The circumference of the circle = 31.4 cm
⇒ 2πr = 31.4
⇒ 2 × 3.14 × r = 31.4
⇒ r = 31.4/2×3.14 = 5 cm
Then area of the circle = πr2 = 3.14 x 5 x 5
= 78.5 cm2
Therefore, the radius and the area of the circle are 5 cm and 78.5 cm2 respectively.
13. A circular flower bed is surrounded by a path 4 m wide. The diameter of the flower bed is 66 m. What is the area of this path? (Take π = 3.14)

Answer
Diameter of the circular flower bed = 66 m
∴ Radius of circular flower bed (r) = 66/2 = 33 m
∴ Radius of circular flower bed with 4 m wide path (R) = 33 + 4 = 37 m
According to question,
Area of path = Area of bigger circle - Area of smaller circle
= πR2 - πr2 = π(R2 - r2)
= π[(37)2 - (33)2]
= 3.14[(37+33) (37+33)] [∴ a2 - b2 = (a+b)(a-b)]
= 3.14 x 70 x 4
= 879.20 m2
Therefore, the area of the path is 879.20 m2.
14. A circular flower garden has an area of 314 m2. A sprinkler at the centre of the garden can cover an area that has a radius of 12 m. Will the sprinkler water the entire garden? (Take π = 3.14)
Answer
Circular area covered by the sprinkler = πr2
= 3.14 × 12 × 12
= 3.14 × 144
= 452.16 m2
Area of the circular flower garden = 314 m2
As Area of the circular flower garden is smaller than area with a sprinkler. Therefore, the sprinkler will water the entire garden.
15. Find the circumference of the inner and the outer circles, shown in the adjoining figure. (Take π = 3.14)

Answer
Radius of outer circle (r) = 19 m
Circumference of outer circle = 2πr = 2 × 3.14 × 19 = 119.32 m
Now radius of inner circle (r') = 19 - 10 = 9 m
∴ Circumference of inner circle = 2πr' = 2 × 3.14 × 9 = 56.52 m
Therefore, the circumferences of inner and outer circles are 56.52 m and 119.32 m respectively.
16. How many times a wheel of radius 28 cm must rotate to go 352 m? (Take π = 22/7)
Answer
Let wheel must be rotated n times of its circumference.
Radius of wheel = 28 cm and Total distance = 352 m = 35200 cm
∴ Distance covered by wheel = n x circumference of wheel
⇒ 35200 = n×2πr
⇒ 35200 = n×2× 22/7 × 28
⇒ n = 35200×7/2×22×28
⇒ n = 200 revolutions
Thus, the wheel must rotate 200 times to go 352 m.
17. The minute hand of a circular clock is 15 cm long. How far does the tip of the minute hand move in 1 hour? (Take π = 3.14)
Answer
In 1 hour, minute hand completes one round means making a circle.
Radius of the circle (r) = 15 cm
A circumference of circular clock = 2πr
= 2 × 3.14 × 15
= 94.2 cm
Therefore, the tip of the minute hand moves 94.2 cm in 1 hour.
Exercise 11.4
1. A garden is 90 m long and 75 m broad. A path 5 m wide is to be built outside and around it. Find the area of the path. Also find the area of the garden in hectares.
Answer
Length of rectangular garden = 90 m and breadth of rectangular garden = 75 m
Outer length of rectangular garden with path = 90 + 5 + 5 = 100 m
Outer breadth of rectangular garden with path = 75 + 5 + 5 = 85 m
Outer area of rectangular garden with path = length × breadth = 100 × 85 = 8,500 m2
Inner area of garden without path = length x breadth = 90 × 75 = 6,750 m2
Now, Area of path = Area of garden with path – Area of garden without path
= 8,500 – 6,750
= 1,750 m2
Since, 1m2 = 1/10000 hectares
Therefore, 6,750 m2 = 6750/10000 = 0.675 hectares
2. A 3 m wide path runs outside and around a rectangular park of length 125 m and breadth 65 m. Find the area of the path.
Answer
Length of rectangular park = 125 m
Breadth of rectangular park = 65 m
Width of the path = 3 m
Length of rectangular park with path = 125 + 3 + 3 = 131 m
Breadth of rectangular park with path = 65 + 3 + 3 = 71 m
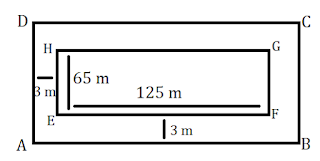
∴ Area of path = Area of park with path - Area of park without path
= (AB × AD) - (EF x EH)
= (131 × 71) - (125 × 65)
= 9301 - 8125 = 1,176 m2
Thus, area of path around the park is 1,176 m2.
3. A picture is painted on a cardboard 8 cm long and 5 cm wide such that there is a margin of 1.5 cm along each of its sides. Find the total area of the margin.
Answer
Length of painted cardboard = 8 cm and breadth of painted card = 5 cm
Since, there is a margin of 1.5 cm long from each of its side.
Therefore reduced length = 8 – (1.5 + 1.5) = 8 – 3 = 5 cm

And reduced breadth = 5 - (1.5 + 1.5] = 5 - 3 = 2 cm
Area of margin = Area of cardboard (ABCD) - Area of cardboard (EFGH)
= (AB × AD) - (EF × EH)
= (8 × 5) - (5 × 2)
= 40 - 10
= 30 cm2
Thus, total area of margin is 30 cm2.
4. A verandah of width 2.25 m is constructed all along outside a room which is 5.5 m long and 4 m wide. Find:
(i) the area of the verandah.
(ii) the cost of cementing the floor of the verandah at the rate of Rs 200 per m2.
Answer
(i) The length of room = 5.5 m
Width of the room = 4 m
The length of room with verandah = 5.5 + 2.25 + 2.25 = 10 m
The width of room with verandah = 4 + 2.25 + 2.25 = 8.5 m

Area of verandah = Area of room with verandah – Area of room without verandah
= Area of ABCD – Area of EFGH
= (AB × AD) – (EF × EH)
= (10 × 8.5) – (5.5 × 4)
= 85 – 22
= 63 m2
(ii) The cost of cementing 1 m2 the floor of verandah = Rs 200
The cost of cementing 63 m2 the floor of verandah = 200 × 63 = Rs 12,600.
5. A path 1 m wide is built along the border and inside a square garden of side 30 m. Find:
(i) the area of the path.
(ii) the cost of planting grass in the remaining portion of the garden at the rate of Rs 40 per m2.
Answer
(i) Side of the square garden = 30 m and
Width of the path along the border = 1 m
Side of square garden without path = 30 – (1 + 1) = 30 – 2 = 28 m
Now Area of path = Area of ABCD - Area of EFGH
= (AB × AD) - (EF × EH)
= (30 × 30) - (28 × 28)
= 900 - 784
= 116 m2

(ii) Area of remaining portion = 28 × 28 = 784 m2
The cost of planting grass in 1 m2 of the garden = Rs 40
The cost of planting grass in 784 m2 of the garden = Rs 40 × 784 = Rs 31,360
6. Two cross roads, each of width 10 m, cut at right angles through the centre of a rectangular park of length 700 m and breadth 300 m and parallel to its sides. Find the area of the roads. Also find the area of the park excluding cross roads. Give the answer in hectares.
Answer
Here, PQ = 10 m and PS = 300 m, EH = 10 m and EF = 700 m And KL = 10 m and KN = 10 m

Area of roads = Area of PQRS + Area of EFGH - Area of KLMN
[∵ KLMN is taken twice, which is to be subtracted] = (PS × PQ) + (EF × EH) - (KL × KN)
= (300 × 10) + (700 × 10) - (10 × 10)
= 3000 + 7000 - 100
= 9,900 m2
Area of road in hectares, 1m2 = 1/10000 hectares
∴ 9,900 m2 = 9900/10000 = 0.99 hectares
Now, Area of park excluding cross roads
= Area of park - Area of road
= (AB × AD) - 9,900 = (700 × 300) - 9,900
= 2,10,000 - 9,900
= 2,00,100 m2
= 200100/10000 hectares = 20.01 hectares.
7. Through a rectangular field of length 90 m and breadth 60 m, two roads are constructed which are parallel to the sides and cut each other at right angles through the centre of the fields. If the width of each road is 3 m, find:
(i) the area covered by the roads.
(ii) the cost of constructing the roads at the rate of Rs 110 per m2.
Answer
(i) Here, PQ = 3 m and PS = 60 m, EH = 3 m and
EF = 90 m and KL = 3 m and KN = 3 m

Area of roads = Area of PQRS + Area of EFGH - Area of KLMN
[∵ KLMN is taken twice, which is to be subtracted]
= (PS × PQ) + (EF × EH) - (KL × KN)
= (60 × 3)+ (90 × 3) - (3 × 3)
= 180 + 270 - 9
= 441 m2
(ii) The cost of 1 m2 constructing the roads = Rs 110
The cost of 441 m2 constructing the roads = Rs 110 × 441 = Rs 48,510
Therefore, the cost of constructing the roads = Rs 48,510.
8. Pragya wrapped a cord around a circular pipe of radius 4 cm (adjoining figure) and cut off the length required of the cord. Then she wrapped it around a square box of side 4 cm (also shown). Did she have any cord left? (Take π = 3.14)

Answer
Radius of pipe = 4 cm
Wrapping cord around circular pipe = 2πr
= 2 × 3.14 × 4 = 25.12 cm
Again, wrapping cord around a square = 4 × side
= 4 x 4 = 16 cm
Remaining cord = Cord wrapped on pipe – Cord wrapped on square
= 25.12 – 16
= 9.12 cm
Thus, she is left with 9.12 cm cord.
9. The adjoining figure represents a rectangular lawn with a circular flower bed in the middle. Find:

(i) the area of the whole land.
(ii) the area of the flower bed.
(iii) the area of the lawn excluding the area of the flower bed.
(iv) the circumference of the flower bed.
Answer
Length of rectangular lawn = 10 m, breadth of the rectangular lawn = 5 m
And radius of the circular flower bed = 2 m
(i) Area of the whole land = length x breadth = 10 × 5 = 50 m2
(ii) Area of flower bed = πr2
= 3.14 × 2 × 2 = 12.56 m2
(iii) Area of lawn excluding the area of the flower bed = area of lawn - area of flower bed
= 50 - 12.56
= 37.44 m2
(iv) The circumference of the flower bed = 2πr = 2 × 3.1 4 × 2 = 12.56 m.
10. In the following figures, find the area of the shaded portions:
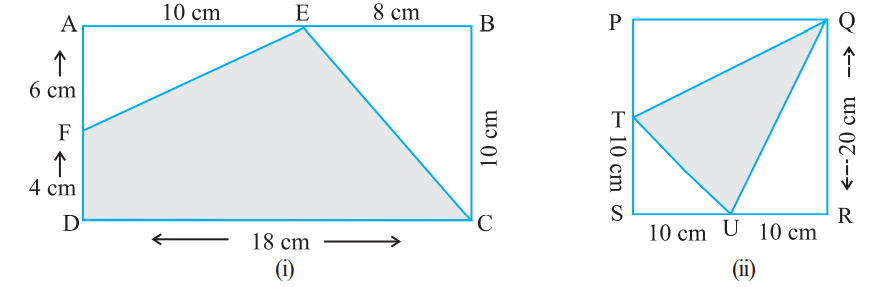
Answer
(i) Here, AB = 18 cm, BC = 10 cm, AF = 6 cm, AE = 10 cm and BE = 8 cm
Area of shaded portion = Area of rectangle ABCD - (Area of Δ FAE + area of Δ EBC}
= (AB × BC) - (1/2 × AE × AF × + 1/2 × BE × BC)
= (18×10) - (1/2 × 10 × 6 + 1/2 × 8 × 10)
= 180 - (30+40)
= 180-70
= 110 cm2.
= 110 cm2.
(ii) Here, SR = SU + UR = 10 + 10 = 20 cm, QR = 20 cm
PQ = SR = 20 cm
PT = PS - TS =(20 - 10)cm
TS = 10 cm, SU = 10 cm, QR = 20 cm and UR = 10 cm
Area of shaded region
= Area of square PQRS - Area of ΔQPT - Area of ΔTSU - Area of ΔUQR
= (SR × QR) - 1/2 × PQ × PT - 1/2 × ST × SU -1/2
= 20 × 20 - 1/2 × 20 × 10 - 1/2 × 10 × 10 - 1/2 × 20 × 10
= 400 - 100 - 50 - 100
= 150 cm2
11. Find die area of the equilateral ABCD. Here, AC = 22 cm, BM = 3 cm, DN = 3 cm and BM ⊥ AC, DN ⊥ AC.

Answer
Here, AC = 22 cm, BM = 3 cm, DN = 3 cm
Area of quadrilateral ABCDF = Area of Δ ABC + Area of ΔADC
= 1/2 × AC × BM + 1/2 × AC × DN
= 1/2 × 22 × 3 + 1/2 × 22 × 3
= 3 × 11 + 3 × 11
= 33 + 33
= 66 cm2
Thus, the area of quadrilateral ABCD is 66 cm2.
Go Back To NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions will help you in covering those essential topics. Perimeter is the distance around a closed plane figure. Area is the space occupied by closed plane figure.
• The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. If the three sides are a, b, and c, then perimeter = a+b+c.
• The perimeter of a rectangle is twice the sum of the lengths of its adjacent sides.
• The perimeter of a square with side s units is 4s.
You can find exercisewise NCERT Solutions which will help you in finding specific questions that you're looking for by visiting the link below. There are total 4 exercises in the Chapter 11 which will encourage students to learn new topics.
By taking help from Chapter 11 NCERT Solutions, you can raise the level of quality of your studies and make learning exciting. A student can make themselves aware of the difficulty of questions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapters:
FAQ on Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area
What are the benefits of NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area Class 7 NCERT Solutions?
NCERT Solutions are very important in improving problem skills and understand all the important points of the chapter. A student will learn how to solve a questions efficiently and obtain maximum marks in the exams.
What is a Circle?
A circle is defined as a collection of points on a plane that are at an equal distance from a fixed point on the plane. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle.
What is circumference of Circle?
The distance around a circular region is known as its circumference. Circumference of a circle = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle or , where πd is the diameter of the circle.
What is a Triangle?
A triangle is a polygon with three vertices, and three sides or edges that are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted as ABC.
