NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
You will get NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management on this page which will help students in grasping basic concepts better and faster. These NCERT Solutions are helpful resources that can help you not only cover the entire syllabus but also provide in depth analysis of the topics. These Chapter 1 Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions are prepared as per the accordance of latest CBSE guidelines so you can score maximum marks.
Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management NCERT Questions and Answers serve as beneficial tool that can be used to recall various questions any time. Students should also refer previous year questions and practise test papers and worksheets to assess their key areas. It can be used to enrich knowledge and make lessons for learners more exciting.

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Through these Chapter 1 Class 8 NCERT Solutions of Science, students should not waste time and adopt a strategy that helps them operate and learn at maximum efficiency. It will be useful in building a great foundation of concepts and make easy for the students to understand basics. Students can cross check their answers and also whether they learned it properly or not.
| Study Material for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management |
|---|
|
Page No: 13
Exercises
1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is ________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _________ and _________ from the soil are essential.
Answer
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
Page No: 14
2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
A
|
B
|
||
(i)
|
Kharif
crops
|
(a)
|
Food
for cattle
|
(ii)
|
Rabi
crops
|
(b)
|
Urea
and super phosphate
|
(iii)
|
Chemical
fertilisers
|
(c)
|
Animal
excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste
|
(iv)
|
Organic
manure
|
(d)
|
Wheat,
gram, pea
|
(e)
|
Paddy
and maize
|
Answer
A
|
B
|
||
(i)
|
Kharif
crops
|
(e)
|
Paddy
and maize
|
(ii)
|
Rabi
crops
|
(d)
|
Wheat,
gram, pea
|
(iii)
|
Chemical
fertilisers
|
(b)
|
Urea
and super phosphate
|
(iv)
|
Organic
manure
|
(c)
|
Animal
excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste
|
3. Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer
(a) Kharif crop: Paddy, maize
(b) Rabi crop: Wheat, gram
4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Answer
(a) Preparation of soil is the first step before growing of crop. It helps to turn the soil and loosen it to allow the root to penetrate deep into it. The loosening of the soil helps in the growth of several soil microbes, earthworms etc., which enrich the soil with humus and other essential nutrients. The process of turning and loosening is called ploughing.This is done using a plough, hoe and cultivators.
(b) Sowing is the process of putting the seeds into the soil for growing crops. We need to use quality seeds for sowing. Sowing is done manually are mechanical equipment like Seed Drill. Seeds of few plants like rice is first grown in a separate area and then transplanted in the fields.
(c) In a field many other undesirable plants may grow along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds. Farmers use many ways to remove weeds. Methods to control weeds are: Tilling before sowing of crops, physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, using certain chemicals called weedicides etc.
(d) Threshing is the process of separating grains or seeds from chaff. It is done after harvesting the crop. It is usually carried out with the help of a machine known as 'Combine'. This machine is a combined harvester and thresher. It harvests plants as well as cleans grains.
5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer
Fertiliser
|
Manure
|
Fertilisers are
commercially available plant nutrients.
|
Manure is a natural
substance prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and
plant wastes.
|
They can be organic
or inorganic in nature.
|
Manure is known to
have a large quantity of organic materials and very little amount
of plant nutrients.
|
They ensure healthy
growth and development of plants by providing them with nitrogen,
phosphorus, potassium, etc.
|
They help in
enriching the soil with organic matter and nutrients.
|
The addition of
fertilisers to the soil requires special guidelines such as dose
time, post addition precautions, etc., to be followed.
|
The addition of
manure does not require any special guidelines.
|
A fertiliser does
not provide any humus to the soil.
|
Manure provides
humus to the soil and increases soil fertility.
|
Its excessive use
causes water pollution. It cannot replenish organic matter of
soil.
|
It protects the
environment and helps in recycling farm waste.
|
6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer
Supply of water to crops at appropriate intercals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation varies according to different seasons, crops, and soil types.
Two methods of irrigation which help in conservation of water are:
→ Sprinkler system: This system is more useful on uneven land, having fewer water supplies. In this method, water is supplied using pipes to one or more central locations within the field. When water is allowed to flow under high pressure with the help of a pump, it gets sprinkled on the crops.
→ Drip system: In this system, water is delivered at or near the roots of plants, drop by drop. This is the most efficient method of irrigation as there is no wastage of water at all. This method is important in areas where water availability is poor.
→ Sprinkler system: This system is more useful on uneven land, having fewer water supplies. In this method, water is supplied using pipes to one or more central locations within the field. When water is allowed to flow under high pressure with the help of a pump, it gets sprinkled on the crops.
→ Drip system: In this system, water is delivered at or near the roots of plants, drop by drop. This is the most efficient method of irrigation as there is no wastage of water at all. This method is important in areas where water availability is poor.
7. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer
If wheat is sown in the kharif season (from June to October), then the whole crop might get destroyed because of many factors such as lack of optimum temperature, adaptability, availability of pests, etc. Kharif season includes the rainy season, which is not favourable for the growth of wheat crop. Therefore, wheat crop should not be sown during this season.
8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer
If continuous plantation of crops is done in the fields then the soil will become poor in necessary nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc. Plants require nutrients for their proper growth and functioning. When a farmer continues to grow crops one after the other, then all nutrients available in the soil reduce and the crop yield decreases automatically.
9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer
Weeds are unwanted wild plants that grow in the field. Weeds compete with the crop for nutrients, light, and space. As a result, crop plants get lesser nutrients, light, and space for their development.
Some important weeding methods are:
→ Weeds can be controlled using weedicides. It is a chemical, which is sprayed in the fields to kill all available weeds. Weedicides are not harmful to crops.
→ Tilling before sowing of crops also helps in removing weeds. Tilling uproots the weeds. The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
→ The manual method of removing weeds is with the help of a khurpi. It involves regular uprooting or cutting of weeds close to the ground.
10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.

Answer

Page No: 15
11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
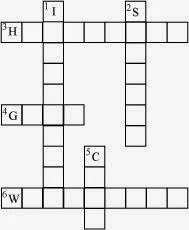
Answer
1. IRRIGATION
2. STORAGE
5. CROP
Across
3. HARVESTOR
4. GRAM
6. WINNOWING

Go Back To NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
These NCERT Solutions are curated by the experts in a comprehensive which can be helpful in clearing your doubts instantly. It will be useful in expanding student's horizon as it cover variety of questions. Chapter 1 Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions can pinpoint your weaknesses and prepare accordingly to change it in a positive way.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management - Topics
• Agricultural Practices
• Basic Practices of Crop Production
• Preparation of Soil
→ Agricultural Implements
• Sowing
→ Selection of Seeds
• Adding Manure and Fertilisers
• Irrigation
→ Traditional Methods of Irrigation
→ Modern Methods of Irrigation
• Protection from Weeds
• Harvesting
• Storage
Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management NCERT Questions and Answers- Notes
• When plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop.
• The crops which are sown in the rainy season (June to September) are called kharif crops.
• The crops grown in the winter season (October to March) are called rabi crops.
• Various tasks performed by a farmer to produce a good crop are called agricultural practices. These are:
→ Preparation of soil
→ Sowing
→ Use of manure and fertiliser
→ Irrigation of crops
→ Protection from weeds
→ Harvesting
→ Storage of food grain.
• Preparation of Soil: It is the first step before growing a crop. The loosened soil helps in the growth
of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing. The main tools used for this purpose are the plough, hoe and cultivator.
• Sowing: The process of placing seeds in the soil is known as Sowing. Before sowing, good quality,
clean and healthy seeds of a good variety are selected.
• Use of manure and fertiliser: Continuous growing of crop in the field causes deficiency of mineral nutrients in the soil. So, the manure is added to the soil to make up the deficiency of mineral nutrients. Manure is prepared from cow dung, urine and other wastes.
• Irrigation of crops: The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season. Traditional methods include Moat (pulley-system), Chain pump, Dhekli, Rahat and Modern methods include Sprinkler system and Drip system.
• Protection from weeds: The unwanted plants in the fields are called weeds. The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light.
• Harvesting: The cutting of crop after it is mature is called harvesting. In harvesting, crops are pulled out or cut close to the ground. Harvesting is either done manually by a sickle or by a machine called harvester. The whole process of separation of the grains from the harvested crop is known as threshing.
• Storage of food grain: Farmers store grains in jute bags or metallic bins. However, large scale storage of grains is done in silos and granaries to protect them from pests like rats and insects.
• Food from Animals: Food is also obtained from animals for which animals are reared and provided with proper food, shelter and care. When done on a large scale, it is called animal husbandry.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management - MCQ Questions with Answers
1. Which irrigation system consists of pulleys
a) Sprinkler.
b) Moat.
c) Dhekli.
d) Rahat.
► b) Moat.
2. Harvesting is the method of
a) Uproot weeds.
b) Cutting crops.
c) Cutting matured crops.
d) Uniform placing of crops.
► c) Cutting matured crops.
3. Khurpi is basically used
a) To uproot weeds.
b) To spread seeds.
c) To irrigate crops.
d) As weedicides.
► a) To uproot weeds.
4. For plants NPK is
a) Micro nutrients.
b) Supplementary nutrients.
c) Macro nutrients.
d) None of the above.
► c) Macro nutrients.
5. Which one provides a lot of humus to the soil?
a) Manure.
b) Fertilizers.
c) Rhizobium bacteria.
d) All of the above.
► a) Manure.
6. The management of rearing animals for food and their products is known as
a) Poultry.
b) Agriculture.
c) Animal husbandry.
d) Warehouse.
► c) Animal husbandry.
7. Nabanya is harvesting festival of
a) Andhra Pradesh.
b) Assam.
c) Arunachal Pradesh.
d) West Bengal.
► d) West Bengal.
8. Mustard is an example of
a) Kharif crops.
b) Rabi crops.
c) Fodders.
d) None of the above.
► b) Rabi crops.
9. Manuring of soil is carried out to
a) Replenish the soil with nutrients.
b) Uniformly distribute the soil nutrients.
c) Help soil to pass air through its gap.
d) Rearing farmers friends.
► a) Replenish the soil with nutrients.
10. The bulk amount of seeds are stored in
a) Granaries.
b) Silos.
c) Cotton bag.
d) All of the above.
► b) Silos.
NCERT Solutions are one of the most basic and sought thing but finding NCERT Solutions are that are reliable, accurate and detailed is not an easy task. Thus, NCERT Solutions prepared by our experts will be useful in understanding in depth concepts well. It help students cope with the pressure of the large board examination syllabus.
