NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
You will get NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame which are helpful in passing exams with flying colours. Through these NCERT Solutions, students should not waste time and adopt a strategy that helps them operate and learn at maximum efficiency. It can be used to enrich knowledge and make lessons for learners more exciting.
Given NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science are available in understandable language and encourage students to learn new topics. It is very challenging to score good marks in tests that is why we have prepared Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame NCERT Questions and Answers. Students can cross check their answers and also whether they learned it properly or not.

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
Chapter 6 Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions are one of the most basic and sought thing but finding NCERT Solutions are that are reliable, accurate and detailed is not an easy task. It will let you explore answers of those questions which you're finding difficult to solve. You will develop the ability to identify what improvements and changes need to be made.
| Study Material for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame |
|---|
|
Page No: 75
Exercise
1. List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answer
The conditions required for combustion to take place are:
→ Presence of a fuel
→ Air (or oxygen)
→ Ignition temperature (minimum temperature at which a substance catches fire).
2. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes _________of air.
(b) A liquid fuel used in homes is ___________.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ___________ before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by _________.
Answer
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes pollution of air.
(b) A liquid fuel used in homes is LPG.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ignition temperature before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water.
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes _________of air.
(b) A liquid fuel used in homes is ___________.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ___________ before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by _________.
Answer
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes pollution of air.
(b) A liquid fuel used in homes is LPG.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ignition temperature before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water.
3. Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer
Combustion of fuels like petroleum causes formation of un-burnt carbon particles along with carbon monoxide gas. These harmful pollutants enter the air and cause respiratory diseases. Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) produces these harmful products in very less quantity. It is a comparatively cleaner fuel. Therefore, the use of CNG has reduced pollution in our cities.
4. Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Answer
LPG
|
Wood
|
| It has more calorific value about 55000 kJ/kg | It has less calorific value about 17000 to 22000 kJ/kg |
| It does not cause any environmental problem. |
On burning wood release unburnt carbon particles which cause diseases such as asthma
|
| It is smokeless fuel. | It gives out lot of smoke |
| It is easy to store and can be easily transported in cylinders and pipelines. | It needs a lot of space to store also very difficult to transport. |
| Low Ignition temprature |
High Ignition temprature
|
5. Give reasons.
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Answer
(a) Water is a conductor of electricity, so it can easily conduct electric current and cause danger of electric shocks or short-circuits. Therefore, water can not be used to control the fire involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel as it does not produce smoke and un-burnt carbon particles, which cause respiratory problems.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily because it has low ignition temperature but when wrapped around an aluminium pipe its temperature is lowered due to aluminium metal absorbing the heat supplied to paper. So it does not catch fire.
6. Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer
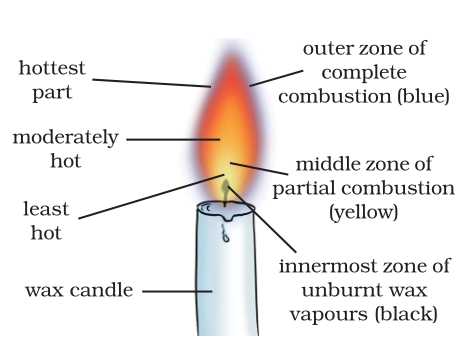
Answer
8. Explain how CO2 is able to control fires.
Answer
Being heavier than oxygen, CO2 covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and
oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled.
9. It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answer
Green leaves have a lot of moisture in them. This moisture does not allow them to catch fire easily. However, dry leaves have no moisturein them. Therefore, they catch fire easily.
10. Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer
A goldsmith uses the outer part of the candle flame for melting gold and silver because in this zone the temperature is the highest which helps to melt these metals easily.
11. In an experiment 4.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer
The calorific value of fuel is the amount of heat produced by the complete combustion of 1 kg of fuel.
Now,
Heat produced by 4.5 kg of fuel = 180000 kJTherefore, heat produced by 1Kg of fuel = 180000/4.5 = 1KJ/Kg
= 40,000 kJ/kg
Hence, the calorific value of the fuel is 40,000 kJ/kg.
12. Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer
Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen and gives out energy during the process in the form of either heat or light or both. Rusting of iron is an exothermic process as heat is released during rusting. Hence, it is a kind of slow combustion.
13. Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the
outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer
The water in the Ramesh's beaker will heat up in a shorter time. This is because the outermost zone of a flame is the hottest zone, while the yellow zone (in which Abida had kept the beaker) is less hot.
Go Back To NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions
These Science NCERT Solutions are curated by the experts in a comprehensive which can be helpful in clearing your doubts instantly. NCERT Textbook will provide you with a lot of interesting topics thus these Class 8 NCERT Solutions will be useful in understanding in depth concepts well.
Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame NCERT Questions and Answers - Topics
• What is Combustion?
• How Do We Control Fire?
• Types of Combustion
• Flame
• Structure of a Flame
• What is a Fuel?
• Fuel Efficiency
→ Burning of Fuels Leads to Harmful Products
Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Notes
• A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat is called combustion.
• The substance that undergoes combustion is said to be combustible. It is also called a fuel. The fuel may be solid, liquid or gas.
• The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called its ignition temperature.
• The substances which have very low ignition temperature and can easily catch fire with a flame are called inflammable substances. Examples of inflammable substances are petrol, alcohol, Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) etc.
• There are three conditions necessary for combustion are fuel, supply of air and ignition temperature.
• Water cools the combustible material so that its temperature is brought below its ignition temperature. This prevents the fire from spreading. Water vapours also surround the combustible material, helping in cutting off the supply of air. So, the fire is extinguished.
• Water works only when things like wood and paper are on fire. If electrical equipment is on fire, water may conduct electricity and harm those trying to douse the fire.
• For fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher. CO2, being heavier than oxygen, covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled. The added advantage of CO2 is that in most cases it does not harm the electrical equipment.
• Liquid carbon dioxide is stored in cylinders. A nozzle is attached to cylinder to release carbon dioxide. When the nozzle is opened, carbon dioxide starts coming out from the cylinder because of high pressure.
• Types of Combustions:
→ Rapid combustion: When combustion occurs rapidly/immediately by applying a flame such as burning of LPG gas in kitchen stove, is known as rapid combustion.
→ Spontaneous combustion: The type of combustion in which a material suddenly bursts into flames, without the application of any apparent cause For example, burning of phosphorus (white) at room temperature, without the effort of burning it.
→ Explosion: A large amount of gas formed in the reaction is liberated. Such a reaction is called explosion.
• The substances which vapourise during burning, give flames. For example, kerosene oil and molten wax rise through the wick and are vapourised during burning and form flames.
• Substances which form vapour during heating, burn with a flame. A flame is a region where combustion of gaseous substances or vapour takes place.
• A good fuel is one which is readily available. It is cheap. It burns easily in air at a moderate rate. There is probably no fuel that could be considered as an ideal fuel.
• The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
• Burning of Fuels Leads to Harmful Products and can cause global warming, acid rain etc.
Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Class 8 Science Questions and Answers - MCQ Questions with answers
1. Amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1kg of fuel is called :
a) energy value
b) combustion value
c) heat value
d) calorific value
► d) calorific value
2. What is the lowest temperature at which a substance starts burning called?
a) Minimum temperature
b) Maximum temperature
c) Boiling temperature
d) Ignition temperature
► d) Ignition temperature
3. Some substances burn on their own when kept exposed in air for some time for example:
a) Sulphur
b) Oxygen
c) Phosphorus
d) Carbon
► c) Phosphorus
4. Lowest temperature at which a substrate catches fire is called its :
a) blackening temperature
b) vaporising temperature
c) threshold temperature
d) ignition temperature
► d) ignition temperature
5. If the temperature falls below its ignition temperature, then what happens to the burning substance?
a) It gets extinguished.
b) It burns brightly.
c) It burns dimly.
d) It burns with smoke.
► a) It gets extinguished.
6. The colour of the hottest part of the flame is:
a) blue
b) black
c) yellow
d) orange
► a) blue
7. A material that burns is one that can combine quickly with:
a) hydrogen
b) oxygen
c) carbon
d) water
► b) oxygen
8. Which of the following is an example of rapid combustion?
a) Candle
b) Cracker
c) White phosphorus
d) Sulphur
► a) Candle
9. Water works as a fire extinguisher by removing:
a) source of combustible substance
b) heat
c) oxygen
d) both oxygen and heat
► d) both oxygen and heat
10. The substances which give heat and light after combustion are called
a) flame
b) fuel
c) combustion
d) none of the above
► b) fuel
Chapter 6 Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions will be useful in gaining good marks in the examinations. It will make entire memorizing process effortless and entertaining. These are very much essential in steering students towards their goal. Given NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science are available in understandable language and encourage students to learn new topics.
