Solutions of How do Organisms Reproduce? Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur SAQ, LAQ, MCQ and HOTS Pg No. 169 Class 10 Biology

39D. Name the contraceptive device used by human females which is put over the cervix.
Answer
→ Diaphragm (or Cap) is a contraceptive device used by human females which is put over the cervix.
40A. Describe the surgical methods of birth control (i) for men, and (ii) for women.
Answer
→ (i) Vasectomy: In male, a small portion of the Vas deferens is removed and both the cut ends are ligated properly. This prevents the sperms from coming out.
(ii) Tubectomy- In female, a small portion of the fallopian tube is removed and the cut ends are ligated. This prevents the entry of ovum into the oviducts.
40B. Name two devices used in the barrier method of birth control.
Answer
→ The barrier methods of birth control are: Condom and Diaphragm
41A. What is meant by contraception ? What are the different methods of contraception ?
Answer
→ Contraception is the prevention of pregnancy by interfering with the normal process of ovulation, fertilisation and implantation.
There are 3 methods of contraception: (i) Barrier method (ii) Chemical method (iii) Surgical method.
41B. What is done in the contraception method known as (i) vasectomy, and (ii) tubectomy?
Answer
→ Contraception is the prevention of pregnancy by interfering with the normal process of ovulation, fertilisation and implantation.
There are 3 methods of contraception: (i) Barrier method (ii) Chemical method (iii) Surgical method.
41C. If a woman is using- copper-T for contraception, will it protect her from sexually transmitted diseases ?
Answer
→ No, using a copper-T will not provide a protection from STD as does not prevent entry of sperm.
42A. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Give two examples of sexually transmitted diseases.
Answer
→ The diseases which are transmitted from infected person to another person by sexual contact are called Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
Examples: AIDS, Syphilis.
42B. Which method of contraception prevents fertilised egg from being implanted in the uterus?
Answer
→ IUCD (Copper - T) prevents the implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
43A. What substances are contained (i) in oral pills, and (ii) in vaginal pills, used as contraceptives? How do they work?
Answer
→ (i) The oral pills contain hormones which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into the oviduct.
(ii) The vaginal pills contain the chemicals called spermicides which kill the sperm.
43B. How does copper-T prevent pregnancy?
Answer
→ Copper-T is effective contraceptive device which is placed inside the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
43C. Name the disease caused by HIV.
Answer
→ HIV is the virus that causes AIDS.
44A. What is the name of surgical method of birth control (or preventing pregnancy) which is carried out (i) in men, and (ii) in women ?
Answer
→ (i) Vasectomy in men and (ii) Tubectomy in women.
44B. Name the part of a seed which (i) contains stored food (ii) grows into root, and (iii) grows into shoot.
Answer
→ (b)
(i) The part of a seed which contains stored food for baby plant is cotyledons.
(ii) The part of a seed which grows into root is radicle.
(iii) The part of a seed which grows into shoot is plumule.
45. Explain how, off springs and parents of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes.
Answer
→ The gametes have half number of chromosomes as compared to that normal body cells. Reduction division (meiosis) takes place during gamete formation which halves the number of chromosomes in both male and female gametes. The original chromosome number (as in parent) is restored after fertilisation in sexual reproduction.
46. In tobacco plant, the male gametes have 24 chromosomes.
(i) What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete?
(ii) What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote?
Answer
→ (i) In tobacco plant, the female gamete have 24 chromosomes.
(ii) In tobacco plant, the zygote have 48 chromosomes.
47A. What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote ?
Answer
→ The ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote is 1:2.
47B. Distinguish between a gamete and a zygote.
Answer
Gamete
|
Zygote
|
It is sex cell or germ cell that takes part in fertilisation.
|
It is a product of fertilisation.
|
It is two types: Male gamete and female gamete
|
It is one type
|
It carries characteristics of only one parent.
|
It carries characteristics of both the parents.
|
48A. Fertilisation in humans can occur only once in a month. Why?
Answer
→ Fertilisation is the process of fusion of male and female gametes. This process occurs once in a month in humans because ovary releases egg (ovulation) once every month.
48B. What is the scientific name of (i) womb, and (ii) birth canal?
Answer
→ (i) The scientific name of womb is ‘uterus’.
(ii) The scientific name of birth canal is ‘vagina.
49. The diagram shows female reproductive system. Name the parts labeled A to D.

(a) In which part do the sperms enter?
(b) Which part releases the egg?
(c) In which part does fertilisation take place ?
(d) In which part does the foetus develop?
Answer
→ A-Oviduct ; B-Ovary ; C – Uterus ; D – Vagina
(a) Part D (vagina)
(b) Part B (ovary)
(c) Part A (oviduct)
(d) Part C (uterus)
50. Why is it an advantage for the testes to be situated in the scrotal sac outside the main body cavity ? Can you think of one disadvantage ?
Answer
→ The testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum because the temperature of scrotum is less than the normal body temperature which is requires for sperm formation. Being outside the main body cavity, testes are more prone to injury.
51. Which structures in human female are equivalent to the following structures in the male?
(a) testes
(b) vas deferens
(c) penis
In each case say in what respect the structures are equivalent ?
Answer
→ (a) In female, ovaries are equivalent to testes in male because both produce gametes.
(b) Fallopian tubes in females are equivalent to vas deferens in male because both transport gametes.
(c) Vagina in females is equivalent to penis in male because penis discharges sperms and vagina receives sperms.
52. People who die from AIDS are not killed by the virus itself. Explain.
Answer
→ AIDS virus damages the immune system of the body rendering the body weak and prone to infections. Thus, virus does not kill the humans directly.
53A. What is the life support system of a fetus?
Answer
→ The fetus gets nutrition from the mother’s blood through a special tissue called placenta. Thus, placenta act as a life support system of a fetus.
53B. How long does a human baby take to develop before birth?
Answer
→ Human baby takes about nine months to develop before birth.
53C. What is the name of the narrow opening between the uterus and the vagina.
Answer
→ Uterus opens into the vagina through a narrow opening called cervix.
Long Answer Type Questions-Pg-170
54A. What is meant by 'unisexual flowers' and 'bisexual flowers' ? Give two examples of each.
Answer
→ The flowers which have either stamens or carpels are called as unisexual flowers. E.g., Papaya, Watermelon.
The flowers which have both stamens and carpels are called as bisexual flowers. E.g., Hibiscus, Mustard plant.
54B. What is pollination? How does pollination occur?
Answer
→ The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same or another flower is known as pollination. It is done by insects, birds, wind and water.
55A. Draw a neat diagram of a flower showing its various parts. In this diagram mark stem, receptacle, sepals, petals, stamen and carpel.
Answer

55B. What name is given to (i) all the petals of a flower, and (ii) all the sepals of a flower ?
Answer
→ (i) All the petals of a flower collectively called the corolla.
(ii) All the sepals of a flower collectively called the calyx.
55C. What are (i) stamen, and (ii) carpel, in a flower?
Answer
→ (i) Stamen is the male reproductive part of the plant.
(ii) Carpel is the female reproductive part of the plant.
55D. What is the other name of carpel of a flower?
Answer
→ Carpel is also called pistil.
55E. What is the name of yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower ?
Answer
→ The yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower is pollen grain.
56A. What changes are seen in boys at the time of puberty?
Answer
→ Following changes are seen in boys at the time of puberty:
•Hair growth in armpits, genital area, chest and face.
•Formation of beards and moustaches.
•Development of deep hoarse voice.
•Development of reproductive organs.
56B. Name the organs which produce sperms in human males.
Answer
→ Testes produce sperms in human males.
56C. Draw a labelled diagram of the human male reproductive system. With the help of this diagram, describe the working of human male reproductive system ?
Answer
→ The human male reproductive system consists of:
(i) Testes – These are main reproductive organs in male. They are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum. The testes produce male germ cells called sperms. It also produces male sex hormones called testosterone.
(ii) Scrotum – It is a muscular pouch which houses the testes. It is present outside the abdominal cavity and maintains a lower temperature than the normal body temperature.
(iii) Epididymis – It is a coiled tube which stores the sperms temporarily.
(iv) Vas Deferens - It is a long tube which carries the sperms from epididymis to another tube called urethra.
(v) Seminal vesicles and prostate gland – The secretion of seminal vesicles and prostate glands pass out along with sperms. These secretions provide a fluid medium for the movement of sperms.
(vi) Penis - It is an organ which passes the sperms from the man's body into the vagina in the women's body during mating.

56D. What is the role of seminal vesicles and prostrate gland in human male reproductive system?
Answer
→ The secretion of seminal vesicles and prostate glands provide a fluid medium for the movement of sperms.
57A. What changes are seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Answer
→ Following changes are seen in girls at the time of puberty:
•Hair growth in armpit and genital area.
•Beginning of menstrual cycle.
•Increase in breast size and darkening of skin of the nipples present at the tips of the breasts.
•Increase in size of uterus and ovary.
57B. Name the organs which produce ova (or egg cells) in human females.
Answer
→ Ovaries produce ova ova (or egg cells) in human females.
57C. Draw a labelled diagram of the human female reproductive system. With the help of this diagram, explain the working of human female reproductive system.
Answer
→ The human female reproductive system consists of:
(i) Ovaries - These are the primary reproductive organs in women. They are oval shaped and present inside the abdominal cavity of a woman. The ovaries produce ova or female gametes and sex hormones called Oestrogen and Progesterone.
(ii) Fallopian tubes (or Oviducts) - These are paired tubes which have funnel shaped openings that cover the ovaries. The ovum released by an ovary goes into the oviduct through its funnel shaped opening. The fertilisation of egg by a sperm takes place in it.
(iii) Uterus - It is an elastic bag- like structure in which the fertilised egg develops into a baby. The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
(iv) Vagina - It is a tubular structure. It receives the sperms for the fertilisation. It is also called birth canal because it is the passage through which the baby is born.
57D. Describe the process of fertilisation in humans and development of embryo briefly.
Answer
→ The fusion of male gamete (sperm) with the female gamete (ova) is known as fertilisation. The process of fertilisation takes place in the fallopian tube. As sperm enter into the vagina through the process of copulation; it moves upwards and enter into the oviduct. In the oviduct, ovum fuse with the sperm to form zygote. The zygote (fertilised egg) get implanted in the inner lining of uterus and undergoes repeated division forming an embryo.
This embryo gets all the requirements from the mother’s body through a special tissue called placenta.
58A. What is ovulation? How often does it happen in human females?
Answer
→ The process of release of ovum from the ovary is called ovulation. It occurs in the 14th day of menstrual cycle.
58B. Where does fertilisation take place in human females ?
Answer
→ The fertilisation takes place in oviducts in females.
58C. Explain why, fertilisation is possible if mating takes place during the middle of menstrual cycle.
Answer
→ Fertilisation is possible if mating takes place during the middle of menstrual cycle because the process of ovulation usually takes place on the 14th day of the beginning of menstrual cycle.
58D. What is meant by implantation ?
Answer
→ The embedding of foetus to the inner lining of uterus is celled implantation.
58E. What is placenta ? What is its function ?
Answer
→ Placenta is a special tissue between developing foetus and uterine wall through which the foetus gets all the requirements from the mother's body.
58F. What joins embryo to placenta in mother's body?
Answer
→ Umbilical cord joins embryo to placenta in mother’s body.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)-Pg-171
59. The anther contains :
A. sepals
B. ovules
C. carpel
D. pollen grains
Answer
→ The yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower is pollen grain.
60. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
A. ovary
B. uterus
C. vas deferens
D. oviducts
Answer
→ The female reproductive system in human beings consists of a pair of ovaries, oviducts and the uterus. Vas deferens is the part of male reproductive system.
61. One of the following is not a part of the human male reproductive system. This is :
A. testis
B. oviduct
C. seminal vesicle
D. prostate gland
Answer
→ Testis, seminal vesicle and prostate gland are part of male reproductive system in human. Oviduct is a part of female reproductive system.
62. Which of the following is not a sexually transmitted disease ?
A. gonorrhoea
B. hepatitis
C. syphilis
D. AIDS
Answer
→ AIDS, Syphilis and gonorrhea are examples of sexually transmitted diseases. Hepatitis is not sexually transmitted disease.
63. Which of the following method of contraception protects a person from acquiring a sexually transmitted disease?
A. oral pills
B. condom
C. copper-T
D. surgery
Answer
→ Sexually transmitted diseases are prevented to some extent by using condoms.
64. In which one of the following birth control methods, a small portion of oviducts of a woman is removed by surgical operation and the cut ends are ligated ?
A. copper-T
B. tubectomy
C. vasectomy
D. diaphragm
Answer
→ Tubectomy is the surgical method of birth control in human females in which the oviducts are cut and ligated (tied) at both ends.
65. One of the following is a surgical method which prevents the sperms from reaching the ovum and pregnancy does not occur. This method is :
A. IUCD
B. vasectomy
C. condom
D. tubectomy
Answer
→ It is a surgical method to block the gamete transfer. It is done in males. In this method, a small portion of the Vas deferens is removed by surgical operation and both the cut ends are ligated properly. This prevents the sperms from coming out.
66. Fertilisation results immediately in the formation of :
A. a zygote
B. an embryo
C. a placenta
D. a foetus
Answer
→ The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation. Zygote is formed in the process of fertilisation.
67. Which one of the following best describes the function of the umbilical cord? It :
A. feeds the embryo with digested substances.
B. conveys nutrients and wastes to and from the embryo respectively
C. removes waste matter from the embryo to the mother's blood.
D. supplies oxygenated blood from the mother to the embryo.
Answer
→ Umbilical cord joins embryo to placenta in mother’s body.
68. The sexually transmitted disease which is caused by bacteria is :
A. malaria
D. diarrhoea
C. gonorrhoea
D. AIDS
Answer
→ Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted disease which is caused by bacteria.
69. AIDS is a deadly disease which is caused by:
A. a protozoan
B. a fungus
C. a bacterium
D. a virus
Answer
→ AIDS is a sexually transmitted disease which is caused by a virus called HIV.
70. The advantage that internal fertilisation has over external fertilisation is that in internal fertilisation:
A. new off-springs are exactly like the parent
B. production of large numbers of gametes is unnecessary
C. copulation and fusion of gametes is passive
D. fewer individuals are produced
Answer
→ The advantage that internal fertilisation has over external fertilisation is that in internal fertilisation, fewer individual are produced.
71. The figure given alongside shows the human male reproductive organs. Which structures make sperms and seminal fluid ?
A. V makes sperms and X makes seminal fluid
B. W makes sperms andY makes seminal fluid
C. X makes sperms and W makes seminal fluid y
D. Y makes sperms and V makes seminal fluid
Answer
→ Y represents teste which produces sperms and V represents seminal vesicle which secrete seminal fluid.
72. In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes are respectively:
A. sepal and anther
B. filament and stigma
C. anther and ovary
D. stamen and style
Answer
→ In a flower, anther produces male gametes and ovary produces female gametes.
73. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower ?
A. pollination, fertilisation, seed, embryo
B. seed, embryo, fertilisation, pollination
C. pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seed
D. embryo, seed; pollination, fertilisation
Answer
→ In flowering plants, the male and female gametes fuse and form zygote. This is called fertilisation. The zygote rapidly grows and develops into embryo and then seed.
74. The characteristics transmitted from parents to offspring are present in:
A. cytoplasm
B. ribosome
C. golgi bodies
D. genes
Answer
→ The characteristics that are transmitted from parents to offspring are present in genes. Genes are present on chromosomes.
75. Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during sexual reproduction show:
A. only similarities with parents
B. only variations with parents
C. both similarities and variations with parents
D. neither similarities nor variations with parents
Answer
→ Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during sexual reproduction show both similarities and variations with parents.
76. The number of chromosomes in parents and off springs of a particular species remains constant due to :
A. doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
B. halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
C. doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
D. halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
Answer
→ The gametes have half number of chromosomes as compared to that normal body cells. Reduction division (meiosis) takes place during gamete formation which halves the number of chromosomes in both male and female gametes. The original chromosome number (as in parent) is restored after fertilisation in sexual reproduction.
77. The length of pollen tube depends on the distance between :
A. pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
B. pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
C. pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
D. upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
Answer
→ The length of pollen tube depends on the distance between pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule.
78. Which of the following statements are true for flowers ?
(i) flowers are always bisexual
(ii) they contain sexual reproductive organs
(iii) they are produced in all groups of plants
(iv) after fertilisation they give rise to fruits
A. (i) and (iv)
B. (ii) and (iil)
C. (i) and (iii)
D. (ii) and (iv)
Answer
→ Flowers are reproductive part of the plants because they contain sexual reproductive organs. These organs produce gametes which take part in the process of fertilisation and form zygote which give rise to fruits.
79. The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for the transport of sperms is:
A. testis vas deferens urethra
B. testis ureter urethra
C. testis urethra ureter
D. testis vas deferens ureter
Answer
→ Testes produces sperms or germ cells. The sperms transfer into epididymis from where vas deferens carries the sperms to another tube called urethra.
80. In human males, the testes lie in the scrotam outside the body because it helps in the:
A. process of mating
B. formation of sperms
C. easy transfer of sperms
D. all the above
Answer
→ The testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum because the temperature of scrotum is less than the normal body temperature which is requires for sperm formation.
81. Which among the following are not the functions of testes at puberty?
(i) formation of germ cells
(ii) secretion of testosterone
(iii) development of placenta
(iv) secretion of estrogen
A. (i) and (ii)
B. (i) and (iii)
C. (ii) and (iv)
D. (iii) and (iv)
Answer
→ The function of testes at the stage of puberty are:
A. To produce germ cells (sperms)
B. To produce male sex hormone, testosterone.
82. During adolescence, several changes occur in the human body. Mark one change from the following associate with sexual maturation in boys:
A. loss of milk teeth
B. increase in height
C. cracking of voice
D. weight gain
Answer
→ The human body undergoes several changes during adolescence. These changes mark the onset of puberty. The change which is associated with sexual maturation in boys is cracking of voice.
83. In human females, an event that indicates the onset of reproductive phase is :
A. growth of body
B. change in hair pattern
C. change in voice
D. menstruation
Answer
→ In human females, menstruation indicates the onset of reproductive phase.
84. The off springs formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because :
A. sexual reproduction is lengthy process
B. genetic material comes from two parents of different species
C. genetic material comes from two parents of same species .
D. genetic material comes from many parents
Answer
→ In sexual reproduction, offspring has lot of variation because DNA of both individuals (male and female) get combine. Due to lot of variations, sexual reproduction allows species to change to more advanced forms from one generation to the next and speed up evolution.
85. One of the following occurs in the reproductive system of flowering plants as well as that of humans. This is :
A. vas deferens
B. anther
C. ovary
D. style
Answer
→ Ovary is the structure that occurs in the reproductive system of flowering plants as well as of humans. In both of them, it produces female gametes called egg.
86. Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross pollination
(iv) Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
A. (i) and (iv)
B. (ii), (iii) and (iv)
C. (ii) and (iii)
D. (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
→ Unisexual flowers have either stamen or pistil. They exhibit cross-pollination. Unisexual flowers which have only stamens cannot produce fruits.
87. Which of the following statements are true for sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
(i) it requires two types of gametes
(il) fertilisation is a compulsory event
(iii) it always results in the formation of zygote
(iv) offsprings formed are clones
A. (i) and (iv)
B. (i), (ii) and (iv)
C. (i), (ii) and (iii)
D. (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
→ During the sexual reproduction in flowering plants, male and female gametes fuse to form zygote. This process is known as fertilisation.
88. One of the following process does not lead to the formation of clones. This is:
A. fission
B. fertilisation
C. fragmentation
D. tissue culture
Answer
→ Fertilisation is the fusion of male and female gametes to form zygote. It does not lead to the formation of clones.
89. In the figure given alongside, the parts marked A, B and C are sequentially:
A. cotyledon, plumule and radicle
B. plumule, radicle and cotyledon
C. plumule, cotyledon and radicle
D. radicle, cotyledon and plumula
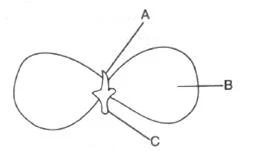
Answer
→ In the given picture, A represents the plumula, B represents the cotyledon and C represents the radicle.
90. The correct sequence of reproductive stages occurring in flowering plants is :
A. gametes, zygote, embryo, seed
B. zygote, gametes, embryo, seed
C. seed, embryo, zygote, gametes
D. gametes, embryo, zygote, seed
Answer
→ In flowering plants, the male and female gametes fuse to form zygote. The zygote rapidly grows and develops into embryo and then seed.
91. The part of a seed which grows and develops into root on germination is:
A. cotyledon
B. plumule
C. follicle
D. radicle
Answer
→ The radicle is the part of a seed which grows and develops into root on germination.
92. The male gametes in a flower and in a human are produced respectively in:
A. stigma and ovary
B. anther and style
C. ovary and testes
D. anther and testes
Answer
→ In a flower, male gametes are produced in anther whereas in a human, male gametes (sperms) are produced in testes.
94. The ratio of number of chromosomes in a human zygote and a human sperm is:
A. 2 : 1
B. 3 : 1
C. 1 : 2
D. 1 : 3
Answer
→ The ratio of number of chromosomes in a human zygote and a human sperm is 2:1.
94. The normal body cell of an organism contains 28 pairs of chromosomes. The number of chromosomes present in its germ cell will be :
A. 28
B. 14
C. 56
D. 42
Answer
→ The normal body cell of an organism contains 28 pairs of chromosomes. The number of chromosomes present in its germ cell will be 14.
Questions Based on High Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)-Pg-173
95. The flask-shaped organ A at the centre of a flower is surrounded by a number of little stalks B having swollen tops which lie just inside the ring of petals.
(a) Name A. What are the various parts of A?
(b) Which part of A contains gametes?
(c) Name B. What is the swollen top of B known as ?
(d) What does the swollen top of B contain ?
(e) Out of A and B, which one is (i) male part, and (ii) female part of the flower?
Answer
→ (a) A is carpel (or pistil). The various parts of carpel (A) are stigma, style and ovary.
(b) Ovary contains gametes.
(c) B is stamen. The swollen top of stamen is known as anther.
(d) Anther contains pollen grains.
(e) (i) B is male part (ii) A is female part of the flower.
96. When an insect sits on the flower of a plant then some particles A present in the top of little stalks in the flower attach to its body hair. When this insect now sits on the flower of another similar plant, then particles A attached to the hair of insect are put on the top of a flask-shaped organ at the centre of flower. The particle A grows a long tube B from the top of flask-shaped organ through which C moves down and reaches the bottom part of flask-shaped organ. Here C fuses with the nucleus of D contained in structure E. The fusion of C and D forms a new cell F which grows and develops into a seed of the plant.
(a) What are particles A ? What is the process of transferring A from one flower to another flower of similar plant by the insect known as ?
(b) What is the name of tube B?
(c) What is C which moves down through the tube B?
(d) Name D and E.
(e) What is F ?
Answer
→ (a) A is pollen grains. The process of the transferring pollen grains from one flower to another flower of similar plant by the insect is known as cross-pollination.
(b) Pollen tube
(c) male gamete (C) moves down through the pollen tube (B).
(d) D is female gamete (ovum or egg); E is ovule.
(e) F is fertilised egg (zygote).
97. When a human female reaches a certain age then vaginal bleeding occurs for a few days after regular time intervals.
(a) What is this process known as (i) in scientific terms, and (ii) in everyday language?
(b) At what approximate age this process starts in human females? What is the human female said to have attained at this stage ?
(c) After how much time is this process repeated? For how many days this process usually lasts?
(d) What does the onset of this process in human females signify?
(e) At which particular event in the life of a human female this process stops temporarily but starts again?
(f) At which approximate age of human female this process stops permanently ?
Answer
→ (a) (i) Menstruation (ii) Periods
(b) Menstruation starts at the age of 12-14 years. The state at which human female attains this stage is called puberty.
(c) It is lasts usually for 3 to 5 days.
(d) Menstruation in human females signifies that the reproductive system of human female has started working.
(e) Menstruation stops temporarily at the beginning of pregnancy.
(f) Menstruation stops permanently at the age of 45-50.
98. X and Y are two human beings. The organ A in the reproductive system of X releases a mature gamete B once a month which goes into a tube-like structure C through a funnel-like opening. The organ D in the reproductive system of Y makes and releases gametes E which pass through a duct F and are introduced by an organ of Y, into the body of X. B and E fuse together in C to form a new cell G. The cell G divides repeatedly to form a ball of cells H which gets embedded in the lining of organ I of reproductive system of X where it grows and develops into a baby.
(a) Name (i) organ A, and (ii) gamete B.
(b) Write two names of tube-like structure C.
(c) Name (i) organ D, and (ii) gamete E.
(d) Write two names of duct F.
(e) Name (i) cell G (ii) ball of cells H, and (iii) organ I.
(f) Out of X and Y, which one is (i) male, and (ii) female ?
Answer
→ (a) (i) Organ A is Ovary, and (ii) Gamete B is ovum (or egg).
(b) Two names of C are: Fallopian tube or Oviduct
(c) (i) Organ D is Testis (ii) Gamete E is sperm
(d) Two names of duct F are : Vas deferens or sperm duct.
(e) (i) G is zygote (fertilised egg) (ii) H is embryo (iii) I is uterus.
(f) (i) Y is male (ii) X is female.
99. When a fertilised egg E formed in the oviduct of a human female divides repeatedly to form an embryo, the embryo gets implanted in the thick and soft lining of the uterus. After this a disc-like special tissue T develops between the uterus wall and embryo through which all the requirements of the developing embryo (and foetus) are met from the mother's body. The embryo is connected to the tissue T through a string like structure S.
(a) What is the other name of fertilised egg cell E ?
(b) What is the name of tissue T ?
(c) Name the string-like structure S .
(d) Name two substances which pass from mother's blood to embryo through tissue T and, one type of substance which passes from embryo to mother's blood.
(e) What happens to S when the baby is born ? Why ?
Answer
→ (a) The other name of fertilised egg cell (E) is zygote.
(b) T is placenta.
(c) S is umbilical cord
(d) Nutrients and oxygen from mother’s blood to embryo; and waste substances from embryo to mother’s blood.
(e) When the baby is born, umbilical cord (S) is tied and then cut. It is done to separate the new born baby from the mother’s body.
100. When a female child is born, her ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs (or ova) contained in immature structures A. On maturing, A bursts open and an egg shoots out of the ovary in a process called B. The process B starts in the females at puberty and occurs again and again after a time period x. Before every occurrence of process B, the inner lining of uterus becomes thick and soft with lots of blood vessels in it. When the egg cell gets fertilised by a sperm, then an event C occurs in the life of mature human female which lasts for time period y leading to the birth of baby. If, however, the egg cell released by the ova does not get a sperm to fuse with, then the thick and soft inner lining of uterus breaks down and comes out of the female's body in an event called D. The occurrence of event Dis controlled by chemical substances E
(a) What are A?
(b) What is process B?
(c) What is the time period x?
(d) Name the event C
(e) How much is the time period y?
(f) What is the name of process D?
(g) Name the chemical substances E
Answer
→ (a) A is follicles.
(b) The process (B) is called ovulation.
(c) X is 28 days.
(d) C is pregnancy.
(e) Y is 9 months.
(f) The process (D) is menstruation
(g) E is hormones which are chemical substances.
101. In the surgical method of birth control available for males, the structures A in the reproductive system are cut and ligated (tied up) at both ends. This prevents the reproductive cells B from coming out from the organs C where they are made in the male body. Since B cannot come out from the male body, they cannot fuse with cell D in the body of a female and hence pregnancy is prevented.
(a) What are structures A ?
(b) What are cells B?
(c) Name the organs C.
(d) What is cell D ?
(e) What is the name of this surgical procedure for birth control available to males?
Answer
→ (a) Vas deferens (A)
(b) Sperms (B)
(c) Testes (C)
(d) Egg cell (or Ovum) (D)
(e) Vasectomy
102. In the surgical method of birth control available for human females, the structures P in the reproductive system are cut and ligated (tied up) properly at both ends. This prevents the reproductive cell Q released by an organ R from entering the structures P so that Q is not available to fuse with another reproductive cell S coming from the male reproductive system. In this way, pregnancy is prevented.
(a) What are structures P?
(b) What is cell' Q?
(c) Name the organ R.
(d) What is the reproductive cells?
(e) What is the name of this surgical method of birth control available to females ?
Answer
→ (a) Fallopian tubes (Or oviduct) (P)
(b) Ovum (or egg cell) (Q)
(c) Ovary (R)
(d) Sperms
(e) Tubectomy
103. The human males use a device X made of a very thin rubber sheet as a covering on the male organ to prevent pregnancy. This device traps the gametes Y in it. In order to prevent pregnancy, the human females use a device Z which is a circle of rubber with a metal spring around it. The device Z is put inside the vagina to cover the cervix. It stops Y from going into the uterus.
(a) What is device X ?
(b) What are Y?
(c) Name the device Z.
(d) What is the general name of these methods of birth control (or preventing pregnancy) ?
(e) The use of which contraceptive device, X or Z, can protect the persons from sexually transmitted diseases ?
Answer
→ (a) Condom (X)
(b) Sperms (Y)
(c) Diaphragm (Z)
(d) Barrier methods
(e) X
104. A woman uses pills A as a method of birth control (or preventing pregnancy). The pills A stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into oviducts. Another woman uses pills B as a method of birth control. The pills B kill the sperms and prevent pregnancy.
(a) What do the pills A contain?
(b) What is the common name of pills A ?
(c) What do the pills B contain ?
(d) What is the common name of pills B ?
(e) What is the general name of these methods of birth control?
Answer
→ (a) Hormones (A)
(b) Oral pills (A)
(c) Spermicides
(d) Vaginal pills (B)
(e) Chemical methods
105. A woman uses a device X made of a common metal for preventing pregnancy. This device works by preventing the implantation of fertilised egg cell (or embryo) in the female organ Y.
(a) What are the two names of device X?
(b) Name the organ Y.
(c) Can this method of contraception protect a woman from acquiring a STD?
Answer
→ (a) Copper-T and IUCD
(b) Uterus
(c) No
106. A, B and C are three common STDs. A and C are caused by bacteria whereas B is caused by a virus D. The virus D reduces the immunity of the infected person to such a low level that the person can die of even very mild diseases.
(a) What could A and C be?
(b) What is B?
(c) Name the virus D ?
(d) How can A, B and C be caused ?
(e) Out of A, B and C, which one does not have a definite cure as yet ?
Answer
→ (a) Syphilis and Gonorrhoea
(b) AIDS
(c) HIV
(d) By sexual contact with an infected person
(e) B (AIDS)
107. The germ cell A produced by a person X is round in shape and it fuses with another germ cell B having a long tail and produced by a person Y. The fusion of A and B produces a new cell C. The cell C divides repeatedly and grows inside the organ D of person X to form E in which the body features of the unborn baby are not much developed. E grows further 'to form Fin which the various body features of the unborn baby (like hands, legs, head, eyes, and ears, etc.) can be identified. F grows further and ultimately forms a baby. What are A, B, C, D, E and F ? Out of the two persons X and Y, which one is male and which one female?
Answer
→ A - ovum (or egg cell); B - sperm; C - zygote (fertilised egg); D - uterus; E - embryo; F - foetus; Y - male; X - female
108. Explain why, a human zygote is more likely to grow into an adult than a frog zygote.
Answer
→ In humans, the development of zygote occurs inside the female body. So, it can grow safely into an adult. On the other hand, in frog, zygote grows outside the body in the water of pond or stream where it is very unsafe because it may be eaten up by other aquatic animals.
109. In a bisexual flower, inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Explain.
Answer
→ Bisexual flower consists both stamens (male reproductive part) and carpel (female reproductive part). If in a bisexual flower stamens are removed artificially and carpel remains intact in the flower then, cross-pollination may occur in this flower which may lead to the formation of fruit.
110. In what ways is fertilisation in a plant :
(a) similar to fertilisation in a human?
(b) different from fertilisation in a human?
Answer
→ (a) Similarities: (i) In both plant and human, the fusion of gametes occurs in the female part.
(ii) The male gamete moves towards the female gamete.
(iii) Zygote is formed after the fertilisation which develops into an embryo.
Differences: (i) In plant, pollination bring male and female gametes together whereas in humans this is done by the process of copulation.
(ii) There is no equivalent in a plant to the oviducts in a human.
(iii) In a human, the male gametes(sperms) swim but in a plant self -fertilisation is possible.
