Extra Questions for Class 9th: Ch 6 Tissues (Science) Important Questions Answer Included
Very Short Answer Questions (VSAQs): 1 MarkQ1.What is meristematic tissue?
Answer
Meristematic tissue is capable of dividing and is found in the developing regions of the plant.
Q2. What do you understand by differentiation ?
Answer
Q2. What do you understand by differentiation ?
Answer
When meristematic tissues lose their ability to divide and become permanent in shape, size and function, the process is called differentiation.
Q3. What are stomata?
Answer
Q3. What are stomata?
Answer
Stomata are the small pores present in the epidermis of leaf.
Q4. What do you mean by guard cells ?
Answer
Q4. What do you mean by guard cells ?
Answer
Stomata are enclosed by two kidney-shaped cells which are called guard cells.
Q5. What are vascular bundles?
Answer
Q5. What are vascular bundles?
Answer
Vascular bundles consist of xylem and phloem.
Apical meristems are the meristematic tissues which are found at the growing tips of stems and roots. It increases the length of the stems and roots and is responsible for the growth of plant.
Q3. Name the living component common to both the complex permanent tissues found in plants. What is its function?
Answer
Answer
Answer
Q6. Name the tissue which is responsible for increase in length of stem and root.
Answer
Answer
Apical meristem.
Q7. What is the function of RBCs?
Answer
Q7. What is the function of RBCs?
Answer
Transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide and pH constancy.
Q8. What is the life span of human RBCs ?
Answer
Answer
About 120 days.
Short Answer Questions-I (SAQs-I) : 2 Marks
Q1. (a) What is a tissue? Justify that blood is a tissue.
(b) Identify the meristematic tissues which are located at:
(i) Growing tips of roots and stems.
(ii) The base of the leaves or internodes on
Answer
Q1. (a) What is a tissue? Justify that blood is a tissue.
(b) Identify the meristematic tissues which are located at:
(i) Growing tips of roots and stems.
(ii) The base of the leaves or internodes on
Answer
(a) A group of cells that are similar in structure and work together to achieve a particular function is called a tissue. Blood is a cluster of similar cells and they perform same function in the body, hence blood is a tissue.
(b) (i) Apical meristem.
(b) (i) Apical meristem.
(ii) Intercalary meristem.
Q2. What is apical meristem? What is its function?
Q2. What is apical meristem? What is its function?
Answer
Apical meristems are the meristematic tissues which are found at the growing tips of stems and roots. It increases the length of the stems and roots and is responsible for the growth of plant.
Q3. Name the living component common to both the complex permanent tissues found in plants. What is its function?
Living component common to xylem and phloem tissues is parenchyma. Its function is to store food and help in sideways conduction of water in xylem and food in phloem.
Q4. Name the tissue that makes husk of coconut. Write three characteristics of this tissue.
Q4. Name the tissue that makes husk of coconut. Write three characteristics of this tissue.
Sclerenchymatous tissue. The cells are dead with long and narrow walls thickened due to lignin.
Q5. What is apical meristem? Where is it located? State its functions.
Q5. What is apical meristem? Where is it located? State its functions.
Apical meristem is a kind of meristematic tissue which is present at the growing tips of stems and roots. It increases the length of the stem and the root. These cells are responsible for linear growth of an organ.Example: Root apical meristem and Shoot apical meristem.
Q6. Name the following tissues:
(i) The connective tissue found between the skin and muscles.
(ii) The tissue which connects two bones.
(iii) The epithelial tissue which forms the lining of the kidney tubules.
(iv) The tissue which is present in the veins of leaves.
Answer
Q6. Name the following tissues:
(i) The connective tissue found between the skin and muscles.
(ii) The tissue which connects two bones.
(iii) The epithelial tissue which forms the lining of the kidney tubules.
(iv) The tissue which is present in the veins of leaves.
Answer
(i) Aerolar
(ii) Ligament
(iii) Cuboidal epithelium
(iv) Sclerenchyma.
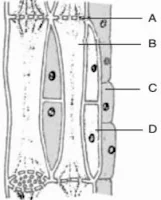
(ii) Identify the parts ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ and ‘D’.
Answer
Short Answer Questions-II (SAQs-II) : 3 Marks
Q1. Classify meristematic tissues on the basis of the region they are present. Also mention their functions.
AnswerQ1. Classify meristematic tissues on the basis of the region they are present. Also mention their functions.
Apical meristems-increase length of stem + roots.
Lateral meristems-increases girth.
Intercalary meristems-increase length, internodes.
Q2. (i) Name the tissue in the following figure:
Lateral meristems-increases girth.
Intercalary meristems-increase length, internodes.
Q2. (i) Name the tissue in the following figure:

(ii) Identify the parts ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ and ‘D’.
Answer
(i) Phloem.
(ii) ‘A’–Sieve plate, ‘B’–Sieve tube, ‘C’–Phloem parenchyma, ‘D’–Companion cell.
Q3. List two characteristics of cork. How is it formed? Mention its role in trees.
Or
List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed?
Answer
(ii) ‘A’–Sieve plate, ‘B’–Sieve tube, ‘C’–Phloem parenchyma, ‘D’–Companion cell.
Q3. List two characteristics of cork. How is it formed? Mention its role in trees.
Or
List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed?
Answer
Mention their role.
(i) Non-living
(ii) Compactly arranged
(iii) No intercellular spaces
A strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis. Cells on the outside are cut forming cork. Protection, makes the plant impervious to gases prevents loss of water, prevents mechanical injury or infection.
Q4 (i) State one point of difference between xylem and phloem.
(i) Non-living
(ii) Compactly arranged
(iii) No intercellular spaces
A strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis. Cells on the outside are cut forming cork. Protection, makes the plant impervious to gases prevents loss of water, prevents mechanical injury or infection.
Q4 (i) State one point of difference between xylem and phloem.
(ii) Draw a neat diagram of xylem vessel and a tracheid.
Answer
(i)Xylem conducts water in the plant body. Phloem transports food in the plant body.
(ii)

Q5. Label the following and give one function of each part labelled (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
(ii)

Q5. Label the following and give one function of each part labelled (i), (ii) and (iii)

Answer
(i) Lateral meristem: for increase in growth of plant parts.
(ii) Intercalary meristem: for formation of leaves, branches etc.
(iii)Apical meristem: increases length of the stem and the root.
(ii) Intercalary meristem: for formation of leaves, branches etc.
(iii)Apical meristem: increases length of the stem and the root.
Long Answer Questions (LAQs) : 5 Marks
Q1. Identify the following tissues:
(i) The epithelial tissue which has pillar like tall cells?
(ii) The cells of this tissue are filled with fat globules.
(iii) The movement of this tissue pushes the mucus forward to clear respiratory tract.
(iv) It gives buoyancy to lotus to help it afloat.
(v) Tissue present in lung alveoli.
Answer
Q1. Identify the following tissues:
(i) The epithelial tissue which has pillar like tall cells?
(ii) The cells of this tissue are filled with fat globules.
(iii) The movement of this tissue pushes the mucus forward to clear respiratory tract.
(iv) It gives buoyancy to lotus to help it afloat.
(v) Tissue present in lung alveoli.
Answer
(i) Columnar
(ii) Adipose
(iii) Ciliated columnar
(iv) Aerenchyma
(v) Squamous.
Q2. (a) Analyse the reason behind the following statements:
(i) Epidermis is thicker in desert plants though it is usually single layered.
(ii) Presence of waxy layer (secreted by epidermis) on the outer surface of plants.
(b) Discuss the cell arrangement which supports the fact that epidermis is a protective tissue.
Answer
(ii) Adipose
(iii) Ciliated columnar
(iv) Aerenchyma
(v) Squamous.
Q2. (a) Analyse the reason behind the following statements:
(i) Epidermis is thicker in desert plants though it is usually single layered.
(ii) Presence of waxy layer (secreted by epidermis) on the outer surface of plants.
(b) Discuss the cell arrangement which supports the fact that epidermis is a protective tissue.
Answer
(a) (i) In desert habitat, protection against water loss is essential. Epidermis is thick in desert plants and are covered with waxy cuticle layer in order to avoid excess loss of water through transpiration due to excess heat.
(ii) The waxy covering aids in protecting the plant against loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion by parasitic fungi.
(b) Epidermis is the outermost covering of cells in plants. It is usually made up of a single layer of cells. On aerial parts of a plant epidermal cells often secrete a waxy, water resistant layer on their outer surface to prevent loss of water from plant. The cells of epidermis are present in a continuous layer without intercellular spaces. Small pores are present on the epidermis of leaf. These pores are called as stomata, which help in gaseous exchange and transpiration. As the plant grows older, a strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of stem and forms a thick cork.
(ii) The waxy covering aids in protecting the plant against loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion by parasitic fungi.
(b) Epidermis is the outermost covering of cells in plants. It is usually made up of a single layer of cells. On aerial parts of a plant epidermal cells often secrete a waxy, water resistant layer on their outer surface to prevent loss of water from plant. The cells of epidermis are present in a continuous layer without intercellular spaces. Small pores are present on the epidermis of leaf. These pores are called as stomata, which help in gaseous exchange and transpiration. As the plant grows older, a strip of secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of stem and forms a thick cork.
