NCERT Solutions for Class 11th: Ch 9 Biomolecules Biology
Page No: 160Exercises
1. What are macromolecules? Give examples.
Answer
Biomolecules with molecular weights more than one thousand Dalton are called macromolecules. These are found in the acid-insoluble fraction. Examples: Protein, polysaccharides, lipids, etc.
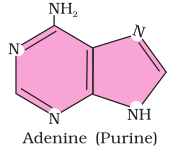
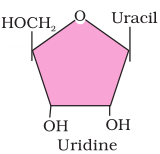
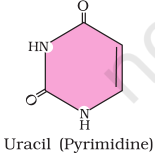
2. Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phospho-diester bond.
Answer
(b) Peptide bond is a covalent bond that joins the two amino acids by - NH - CO linkage.
(c) Phosphodiester bond is a strong covalent bond between phosphate and two sugar groups. Such bonds form the sugar phosphate backbone of nucleic acids.
3. What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins?
Answer
The helical polypeptide chain undergoes coiling and folding to form a complex three-dimensional shape is called tertiary structure of proteins. These coils and folds are arranged to hide the non-polar amino acid chains and to expose the polar side chains. The tertiary structure is held together by the weak bonds formed between various parts of the polypeptide chain.
Answer
1.

2.

3.
4.

5.

6.

7.
8.
9.

10.

Fat and many hormones are manufactured by isolation. Pharmaceutical and consumer goods industry can be the major buyers of these products.
5. Proteins have primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to purity or homogeneity of a protein?

2.

3.

4.

5.

6.

7.

8.

9.

10.

Fat and many hormones are manufactured by isolation. Pharmaceutical and consumer goods industry can be the major buyers of these products.
5. Proteins have primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to purity or homogeneity of a protein?
Answer
Yes, we can connect the given information to purity or homogeneity of a protein. It is known that an accurate sequence of a certain amino acid is very important for the functioning of a protein. If there is any change in the sequence, it would alter its structure, thereby altering the function. If we are provided with a method to know the sequence of an unknown protein, then using this information, we can determine its structure and compare it with any of the known correct protein sequence. Any change in the sequence can be linked to the purity or homogeneity of a protein.
6. Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., cosmetics, etc.)
Answer
List of proteins used as therapeutic agents are Insulin, Oxytocin, Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), Thrombin, Fibrinogen, Renin, Immunoglobulin, Diastase and Streptokinase.
Proteins are also commonly used in the manufacture of cosmetics, toxins, and as biological buffers.
7. Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Answer
Triglycerides are composed of two types of molecules, i.e., glycerol (3 carbon molecules) and fatty acids which attach to the glycerol at the alcohol unit. It is mainly present in vegetable oils and animal fat. The structure is given:
Page No: 161
8. Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yoghurt from your understanding of proteins.
Answer
Milk is converted into curd or yogurt by the process of fermentation. Milk consists of globular proteins. During fermentation, the milk sugar (lactose) produces lactic acid. Lactic acid acts on the globular proteins present in the milk and denatures them. This denaturation destroys the tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins and the globular proteins are converted into fibrous proteins thus giving a thick texture to the milk due to coagulation of the proteins.
9. Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models).
Answer
Yes. The biomolecules can be represented by the ball and stick model. The bonds which hold the atoms are represented by sticks, whereas the atoms are represented by balls.
Example: In the model of D-glucose, the oxygen atoms are represented by red balls, the hydrogen atoms by blue balls, while the carbon atoms are represented by grey balls.
10. Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Answer
Titratinga neutral or basic amino acid against a weak base will dissociate only one functional group, whereas titration between acidic amino acid and a weak acid will dissociate two or more functional groups.
7. Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Answer
Triglycerides are composed of two types of molecules, i.e., glycerol (3 carbon molecules) and fatty acids which attach to the glycerol at the alcohol unit. It is mainly present in vegetable oils and animal fat. The structure is given:
8. Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yoghurt from your understanding of proteins.
Answer
Milk is converted into curd or yogurt by the process of fermentation. Milk consists of globular proteins. During fermentation, the milk sugar (lactose) produces lactic acid. Lactic acid acts on the globular proteins present in the milk and denatures them. This denaturation destroys the tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins and the globular proteins are converted into fibrous proteins thus giving a thick texture to the milk due to coagulation of the proteins.
9. Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models).
Answer
Yes. The biomolecules can be represented by the ball and stick model. The bonds which hold the atoms are represented by sticks, whereas the atoms are represented by balls.
Example: In the model of D-glucose, the oxygen atoms are represented by red balls, the hydrogen atoms by blue balls, while the carbon atoms are represented by grey balls.
10. Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Answer
Titratinga neutral or basic amino acid against a weak base will dissociate only one functional group, whereas titration between acidic amino acid and a weak acid will dissociate two or more functional groups.
11. Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
Answer
Answer
Yes, Fevicol is different from gums as it comprises synthetic polymers.
13. Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine for them.
Answer
Qualitative tests for proteins, amino acids and fats:
• Biuret test: The Biuret test for protein identifies the presence of protein by producing light blue to purple colour of the solution.
• Grease test for oil: Certain oils give a translucent stain on brown paper. This test can be used to show the presence of fat in vegetable oils.
• Ninhydrin test: If Ninhydrin reagent is added to the solution, then the colourless solution changes to pink, blue or purple colour depending on the type of amino acid.
Item
|
Name of the test
|
Procedure
|
Result
|
Inference
|
|
1.
|
Fruit juice
|
Biuret’s test
|
Fruit juice +
Biuret’s reagent
|
Colour changes from
light blue to purple
|
Protein is present.
|
Grease
test
|
To a brown
paper, add a few drops of fruit juice.
|
No translucent spot
|
Fats
and oils are absent or are in negligible amounts.
|
||
Ninhydrin test
|
Fruit juice +
Ninhydrin reagent + boil for 5 minutes
|
Colourless
solution changes to pink, blue, or
purple colour
|
Amino acids are
present.
|
||
2.
|
Saliva
|
Biuret’s test
|
Saliva
+ Biuret’s reagent
|
Colour changes from
light blue to purple
|
Proteins are
present.
|
Grease
test
|
On
a brown paper, add a drop of saliva.
|
No translucent spot
|
Fats/oils
are absent.
|
||
Ninhydrin test
|
Saliva + Ninhydrin
reagent + boil for 5 minutes
|
Colourless solution
changes to pink, blue, or purple colour
|
Amino acids are
present.
|
||
3.
|
Sweat
|
Biuret’s test
|
Sweat + Biuret’s
reagent
|
No colour change
|
Proteins are absent.
|
Solubility test
|
Sweat + Water
|
Oily appearance
|
Fats/oil may be
present.
|
||
Ninhydrin test
|
Sweat + Ninhydrin
reagent + boil for 5 minutes
|
No colour change,
solution remains colourless
|
Amino acids are
absent.
|
||
4.
|
Urine
|
Biuret’s test
|
Few
drops of urine + Biuret’s reagent
|
Colour changes from
light blue to purple
|
Proteins are
present.
|
Solubility test
|
Few drops of urine +
Water
|
Little bit of oily
appearance
|
Fats may or may not
be present.
|
||
Ninhydrin test
|
Few drops of urine +
Ninhydrin reagent + boil for 5 minutes
|
Colourless solution
changes to pink, blue, or purple colour depending on the type of
amino acid
|
Amino acids are
present.
|
||
14. Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere and compare it with how much of paper is manufactured by man and hence what is the consumption of plant material by man annually. What a loss of vegetation!
Answer
Approximately, 100 billion tonnes of cellulose are made per year by all the plants in the biosphere and it takes 17 full grown trees to make one ton of paper. Trees are also used to fulfil the other requirements of man such as for timber, food, medicines, etc. Hence, it is difficult to calculate the annual consumption of plant material by man.
15. Describe the important properties of enzymes.
Answer
Important properties of enzymes are:
→ Enzymes are generally complex macromolecules of globular proteins with high molecular weight.
→ Enzymes do not start a reaction but increase the rate of chemical reaction.
→ Enzyme itself is not used up in the reaction it catalyzes so it can be used over again and again.
→ Enzymes have a high turn over number. It means the number of reactions that an enzyme molecule can catalyze per second.
→ Enzymes are specific in action.
→ The action of enzyme is greatly affected by temperatures. Their activity decreases with increase in temperature.
→ They show maximum activity at an optimum pH of 6 - 8.
→ The velocity of enzyme increases with increase in substrate concentration and then, ultimately reaches maximum velocity.
Go To Chapters







